Having healthy eggs is one of the most important and influential factors on a woman’s fertility. Therefore, ensuring the health and quality of eggs before pregnancy is very important. Most women who have weak oocytes are unable to conceive normally and will inevitably have to use fertility treatments such as IVF. In some cases, the quality of the eggs is so low that the only way to get pregnant is to use donated eggs. Therefore, strengthening the eggs and finding ways to increase their quality is one of the most important concerns before attempting to conceive.
The effect of age on the egg quality

In the past, it was believed that every woman was born with all her ovarian reserves and could not produce more eggs after birth. Therefore, age was the most important factor affecting the health and quality of eggs and with increasing age, the quality and quantity of eggs decreases. But new scientific findings show that stem cells in the ovaries can produce new eggs during the reproductive years. However, it should be noted that age still has an important effect on the process of ovulation and the production of new egg cells, because the production of new oocytes is possible only at the reproductive age, and with increasing age, the possibility of embryo implantation in the uterus decreases.
Although it is not possible to prevent a decrease in fertility and ovulation with aging, there are ways to improve the egg quality and increase the chances of pregnancy at an older age. Factors such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, lifestyle changes and the use of supplements, etc. can have a positive effect on the quality of eggs. Therefore, observing these items is very important to increase the quality of eggs before attempting to conceive, especially at the age of over 40 years.
Factors affecting the quality of egg
The quality of the eggs largely depends on the environment in which the ovary grows. Oocytes usually go through a 90-day period from the beginning of development until they reach puberty and are released from the ovaries. . Therefore, the ovarian environment during these 90 days has a great impact on the quality of the released eggs. In general, women over the age of 40 have a poor ovarian environment to grow quality oocytes. However, following some tips for 3 to 4 months before getting pregnant can help them to increase the quality of eggs and pregnancy health. The most important factors affecting the health and quality of eggs are:
We know that proper diet and nutrition have a direct impact on our health. So it is not surprising that diet may affect the reproductive health and quality of eggs. Women who are planning to become pregnant should eat foods that are high in vitamin A, such as liver, fish, and a variety of high-fat dairy products, to improve the quality of their eggs. Adequate intake of vitamin A by the body contributes to the proper response of the ovaries, increasing the quality of eggs and fetal growth. In addition, research shows that eating omega-3 foods such as fish and flaxseed is effective in maintaining fertility and improving egg quality.
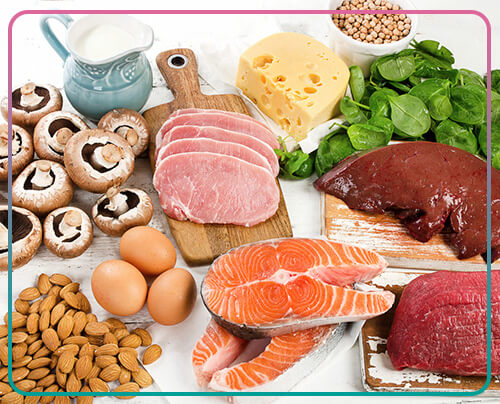

Doctors recommend a low-carb, high-fat diet (unsaturated fat) before pregnancy. This diet helps to improve the quality of eggs in two ways, one is to reduce inflammation and the other is to balance reproductive hormones. Inflammation can cause tissue damage, reduce blood flow to the ovaries, and interfere with the ovaries’ ability to receive nutrients. However, adequate ovarian nutrition and adequate blood flow are essential to ensure the growth of eggs and the production of quality eggs. Therefore, to reduce inflammation, it is recommended to limit carbohydrate intake because the breakdown of carbohydrates in the body causes the production of glucose, fructose, and other sugars that cause inflammation.
The balanced production of reproductive hormones is another factor affecting the quality of eggs. When hormones become unbalanced in the body (a common symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome; PCOS), the ovaries do not function properly and the eggs mature at low speed and quality.
Therefore, to increase the quality of eggs, it is recommended to increase the consumption of unsaturated fats because fat gives energy to the body and helps in the production of hormones and the growth of egg cells. In addition, it is recommended to avoid excessive caffeine consumption because caffeine in various ways impairs women’s reproductive function.
Some simple lifestyle changes can improve egg quality and increase your chances of getting pregnant. Some of these changes are:
No.1 Having enough sleep

Adequate and quality sleep is an important part of a healthy lifestyle. During sleep, the body repairs cells and recovers lost energy. In addition, during sleep, the hormones needed for reproduction are released. Therefore, adequate sleep contributes greatly to the growth and health of the eggs. The brain secretes the hormone melatonin to improve sleep. In addition to improving sleep quality, this hormone also increases egg quality and facilitates ovulation and fetal growth. With age, the level of the hormone melatonin decreases, so in women over 40, it is important to choose methods to improve sleep. Eating a healthy diet, managing stress, and reducing cell phone and TV use can help improve sleep patterns.
No.2 Avoiding alcohol and smoking
Research shows that alcohol consumption and smoking reduce the quality of eggs and increase the number of abnormal eggs. The chemicals in cigarettes cause the DNA of the egg to mutate, which is usually not suitable for fertility. Therefore, avoiding alcohol and smoking has a significant effect on egg health and quality.
No.3 Stress management
Stress causes imbalance and causes many problems in the body. When we are stressed, the body begins to produce the hormones cortisol and prolactin. These hormones can disrupt the ovulation process and prevent the production of quality eggs. The importance of stress management in the infertility treatment process is twofold. Because fertility treatment itself is a stressful process and if this stress is managed properly, it will have a great impact on the success of treatment.
No.4 Exercising
Light exercise such as walking and yoga are great ways to reduce stress, increase blood flow to the genitals and strengthen the immune system. As mentioned earlier, the ovaries need enough blood flow to provide nutrients and oxygen in order to be a good environment for quality eggs to grow. Therefore, exercising helps a lot to increase blood flow and increase the quality of eggs. In addition, drinking at least 8 glasses of water a day and doing abdominal massages increase blood circulation in the ovaries and uterus and improve the quality of eggs.
Using supplements is one of the best options to complete a healthy diet and ensure the health of the body and reproductive health. Supplements can help improve egg quality in women of childbearing age and over 40 years. Research shows that the nutrients and vitamins in supplements increase the ability of the egg to divide and improve the quality of the formed fetus. In addition, the antioxidants in supplements prepare the ovarian environment to improve egg quality.
The most important supplements recommended to improve egg quality in women over 40 are:
Omega-3: Omega-3 helps maintain fertility in women and improves egg quality by delaying ovarian aging. Getting enough omega-3 through your diet is difficult, so it is recommended to take a fish oil supplement that contains adequate amounts of omega-3.
Coenzyme Q10: Coenzyme Q10 (Co Q10) is an antioxidant that enhances the ability of an egg to divide. The level of this enzyme in the body decreases with age. Therefore, supplementation of this enzyme is recommended to improve the quality of eggs and provide the energy needed for egg DNA amplification in women over 40 years of age.
Vitamin A: Vitamin A plays an important role in improving egg quality and fetal growth. Vitamin A supplementation helps women over the age of 40 to ensure proper egg growth.
Other Supplements: Supplements containing vitamin E, zinc, folate, and some B vitamins can also help increase egg quality.
The effect of increasing egg quality on the success of fertility treatments
Paying attention to strategies to improve egg quality is important not only for women who are planning to become pregnant at an older age, but also helps women who intend to use fertility treatments such as IUI, IVF, and ICSI and increases the chances of successful treatment. learn more about the ways that increase the chance of IVF Success: 11 Tips to Increase Your Chances of IVF Success
Infertility treatments using high-quality eggs increase the likelihood of embryo formation. In addition, embryos formed with quality eggs have a better chance of implanting in the uterus and will continue to have more successful cell division.