How prepare for IVF?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology provide information online about U.S. clinics' individual pregnancy and live birth rates.
When choosing an in vitro fertilization (IVF) clinic, keep in mind that a clinic's success rate depends on many factors, such as patients' ages and medical issues, as well as the clinic's treatment population and treatment approaches. Ask for detailed information about the costs associated with each step of the procedure.

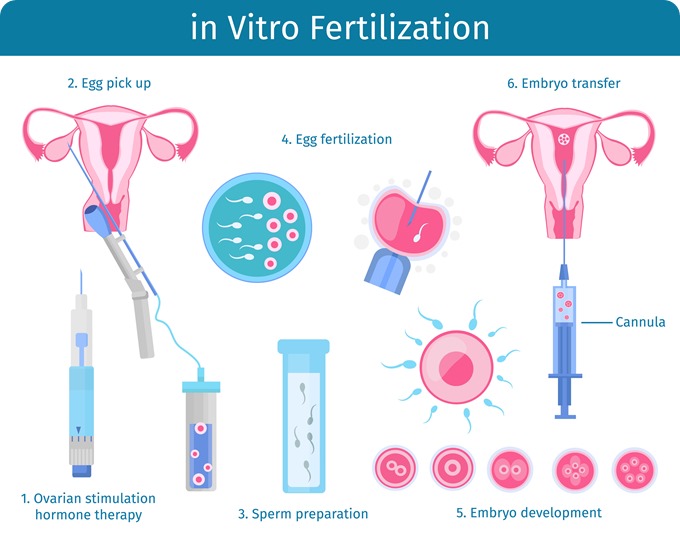
Before beginning a cycle of IVF using your own eggs and sperm, you and your partner will likely need various screenings, including:
- Ovarian reserve testing. To determine the quantity and quality of your eggs, your doctor might test the concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol (estrogen), and anti-mullerian hormone in your blood during the first few days of your menstrual cycle. Test results often used together with an ultrasound of your ovaries, can help predict how your ovaries will respond to fertility medication.
- Semen analysis. If not done as part of your initial fertility evaluation, your doctor will conduct a semen analysis shortly before the start of an IVF treatment cycle.
- Infectious disease screening. You and your partner will both be screened for infectious diseases, including HIV.
- Practice (mock) embryo transfer. Your doctor might conduct a mock embryo transfer to determine the depth of your uterine cavity and the technique most likely to successfully place the embryos into your uterus.
- Uterine exam. Your doctor will examine the inside lining of the uterus before you start IVF. This might involve a sono hysterography — in which fluid is injected through the cervix into your uterus — and an ultrasound to create images of your uterine cavity. Or it might include a hysteroscopy — in which a thin, flexible, lighted telescope (hysteroscope) is inserted through your vagina and cervix into your uterus.
Before beginning a cycle of IVF, consider important questions, including:
- How many embryos will be transferred? The number of embryos transferred is typically based on age and the number of eggs retrieved. Since the rate of implantation is lower for older women, more embryos are usually transferred — except for women using donor eggs or genetically tested embryos. Most doctors follow specific guidelines to prevent higher-order multiple pregnancies — triplets or more — and in some countries, legislation limits the number of embryos that can be transferred. Make sure you and your doctor agree on the number of embryos that will be transferred before the transfer procedure.
- What will you do with any extra embryos? Extra embryos can be frozen and stored for future use for several years. Not all embryos will survive the freezing and thawing process, although most will. Cryopreservation can make future cycles of IVF less expensive and less invasive. Or, you might be able to donate unused frozen embryos to another couple or a research facility. You might also choose to discard unused embryos.
- How will you handle a multiple pregnancies? If more than one embryo is transferred to your uterus, IVF can result in multiple pregnancy — which poses health risks for you and your babies. In some cases, the fetal reduction can be used to help a woman deliver fewer babies with lower health risks. Pursuing fetal reduction, however, is a major decision with ethical, emotional, and psychological consequences.
- Have you considered the potential complications associated with using donor eggs, sperm or embryos, or a gestational carrier? A trained counselor with expertise in donor issues can help you understand the concerns, such as the legal rights of the donor. You may also need an attorney to file court papers to help you become legal parents of an implanted embryo.
- ۰ نظر
- 06 February 21 ، 05:32
- ۲۱۰ نمایش